Conquering Incontinence: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
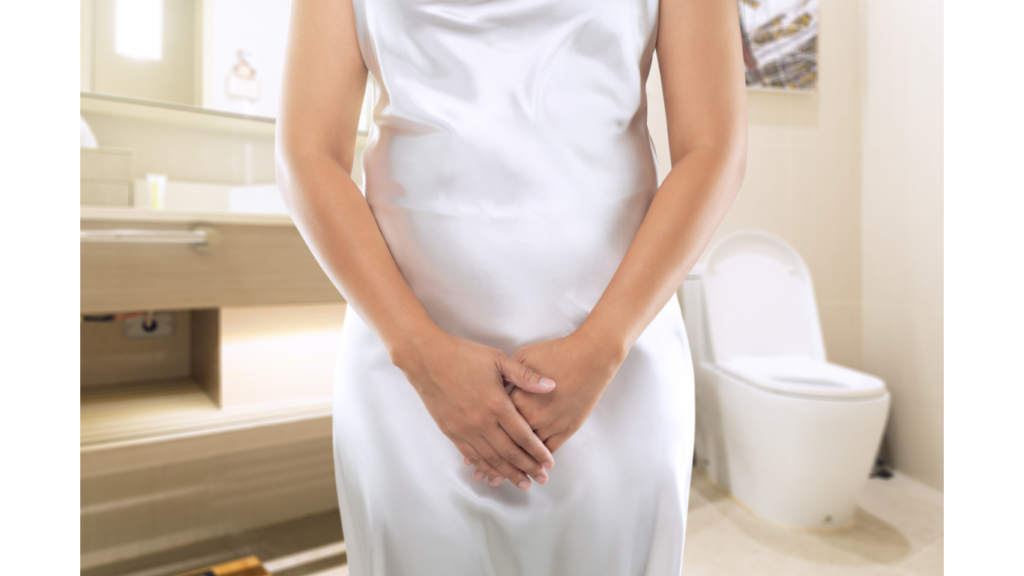

Incontinence refers to the involuntary loss of urine or feces, leading to difficulties in controlling bladder or bowel movements. Here’s some information on the causes, symptoms, and treatments of incontinence:
Causes of Incontinence:
- Weak pelvic floor muscles: Weakened muscles that support the bladder and rectum can contribute to urinary or fecal incontinence.
- Urinary tract infections: Infections in the urinary tract can cause temporary incontinence.
- Nerve damage: Conditions such as diabetes, multiple sclerosis, or spinal cord injuries can disrupt nerve signals involved in bladder and bowel control.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can affect bladder and bowel function.
- Prostate problems: In men, an enlarged prostate or prostate surgery can result in urinary incontinence.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, sedatives, or muscle relaxants, may contribute to incontinence.
- Other factors: Chronic coughing, obesity, constipation, and certain lifestyle habits (e.g., excessive caffeine or alcohol intake) can also play a role in incontinence.
Symptoms of Incontinence:
- Urinary incontinence:
- Stress incontinence: Leakage of urine during activities that increase abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or exercising.
- Urge incontinence refers to a sudden and strong urge to urinate, often followed by an involuntary release of urine.
- Overflow incontinence, on the other hand, involves the continuous or frequent dribbling of urine caused by an overfilled bladder that cannot fully empty.
Fecal incontinence:
- Involuntary passage of stool or inability to control bowel movements.
- Difficulty sensing the need to defecate or lack of awareness of bowel movements.
- Leaking of small amounts of stool or complete loss of bowel control.
Treatments for Incontinence:
- Lifestyle modifications:
- Pelvic floor Physiotherapy: Pelvic Floor exercises strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises like Kegels to improve bladder and bowel control
- Fluid and diet management: Adjusting fluid intake and dietary habits to avoid bladder irritants and regulate bowel movements.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the bladder and pelvic floor muscles.
- Bladder training: Techniques to gradually increase the time between urination and improve bladder control.
- Medications:
- Anticholinergics: Medications that relax the bladder muscle and reduce urinary urgency and frequency.
- Topical creams: Creams or ointments that can help treat skin irritation caused by incontinence.
- Medical devices:
- Pessary: A small device inserted into the vagina to support the bladder or rectum.
- Catheters: Thin tubes used to drain urine from the bladder.
- Nerve stimulation: Electrical stimulation of the nerves involved in bladder and bowel control to improve function and reduce incontinence.
- Surgery: In certain cases, surgical interventions may be recommended to treat underlying anatomical or functional issues causing incontinence.
Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy is an effective solution for alleviating incontinence symptoms, addressing persistent conditions, and expediting the healing process. Licensed Pelvic Floor Physiotherapists evaluate your specific condition and provide personalized recommendations or therapies to help you manage your incontinence symptom effectively